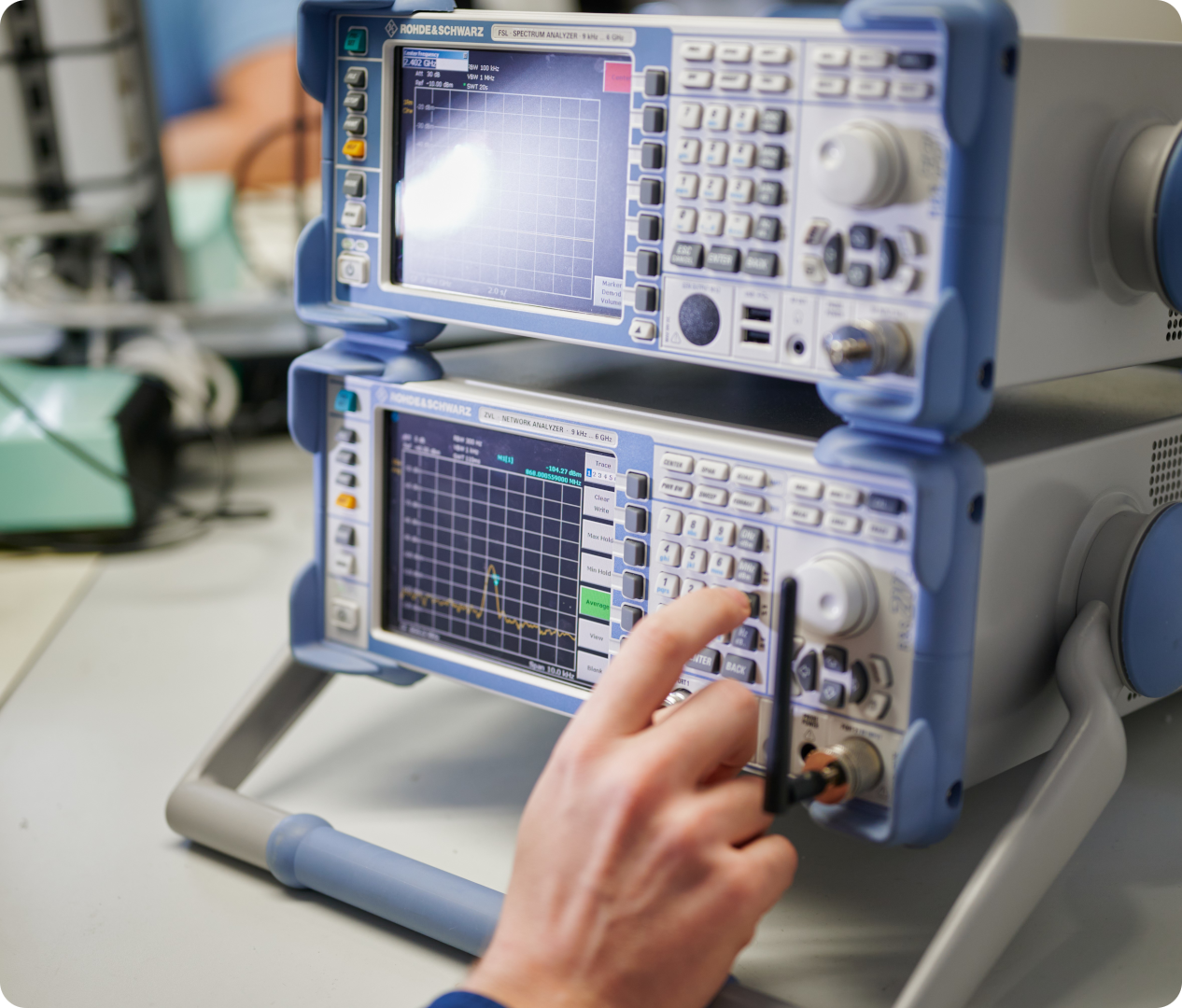
Challenges and Best Practices
Radio frequency (RF) circuitry is a fundamental part in modern electronics. It is also one of the more challenging aspects when introducing a new design to mass production. Well-planned and precise quality control is key to success in radio link quality, cost and time to market.
This AtoMik® White Paper summarizes a few guidelines for radio frequency production test, aimed to support product developers, test development engineers, quality managers and electronics manufacturers.

Test Scope
First, what needs to be verified? Identify and address risks. Is the primary need to verify frequency or power, communication, calibration or just solder joints? A low power protocol like ZigBee or Thread or 5 GHz Wi-Fi? What precision is necessary? What system loss is acceptable?
Test purposes may then dictate a fixture set-up. Precise power measurements and calibration often requires conducted measurements, while radiated tests are quicker to adjust and less prone to mechanical wear.
Instruments, switches, attenuators and cabling should be selected with precision and expected levels in mind, including safety margins for erroneous units.
Design for Test
When adding test points to RF designs, it is important to alter the RF path as little as possible. Avoid stubs and chose a test point style that fits both design constraints and RF probes available. Position the test points to include all relevant components in the test path.
Antennas and traces beyond the test point will of course impact RF path tuning and test levels. When high precision is needed, open test points can be replaced by switch connectors breaking the path at the test point. Sensitive signals such as crystal clocks may be routed via an MCU to a test point to prevent load mismatch.
If possible, place RF test points separated from other test points to allow space for probes and cables. Some probes also require inserts and high mechanical precision.
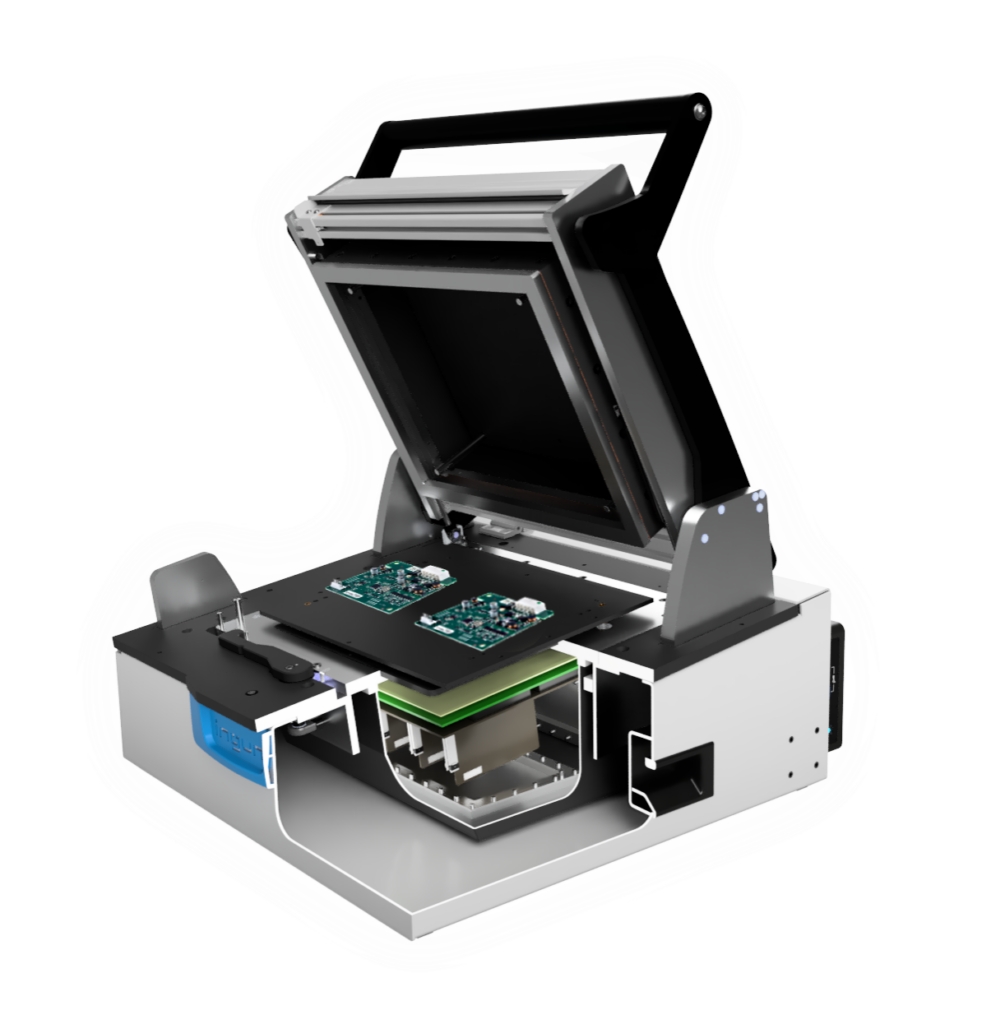

Fixture Set-Up
To reduce noise, RF tests are performed inside a shielded RF box. The box itself also adds complexity, as reflections cause interference patterns and antennas are forced into the transmitter near field. There, the electromagnetic plane wave is not fully developed and prone to detuning.
Due to interference, radiated signal strength varies in different positions in the box. Small mechanical changes may have large effects on test levels. For modulation or communication tests, foam absorbers may be needed.
Cables and equipment have transfer functions as well and test path loss must be considered over frequency. Effects are generally more evident as frequency increases.
Data Analysis
Organizing and understanding test data is crucial for quality control and improvement. The first step is to set test limits depending on design properties, expected precision and test system characteristics. Narrow limits reduce variation between units, but also increase repair and waste costs.
It often makes sense to introduce warning levels aside from failure limits, so that batch drift can be detected before actual errors appear. When properly addressed and analysed, deviation gives valuable information both on unit level and on batch level, but also about probe wear and fixture maintenance needs.
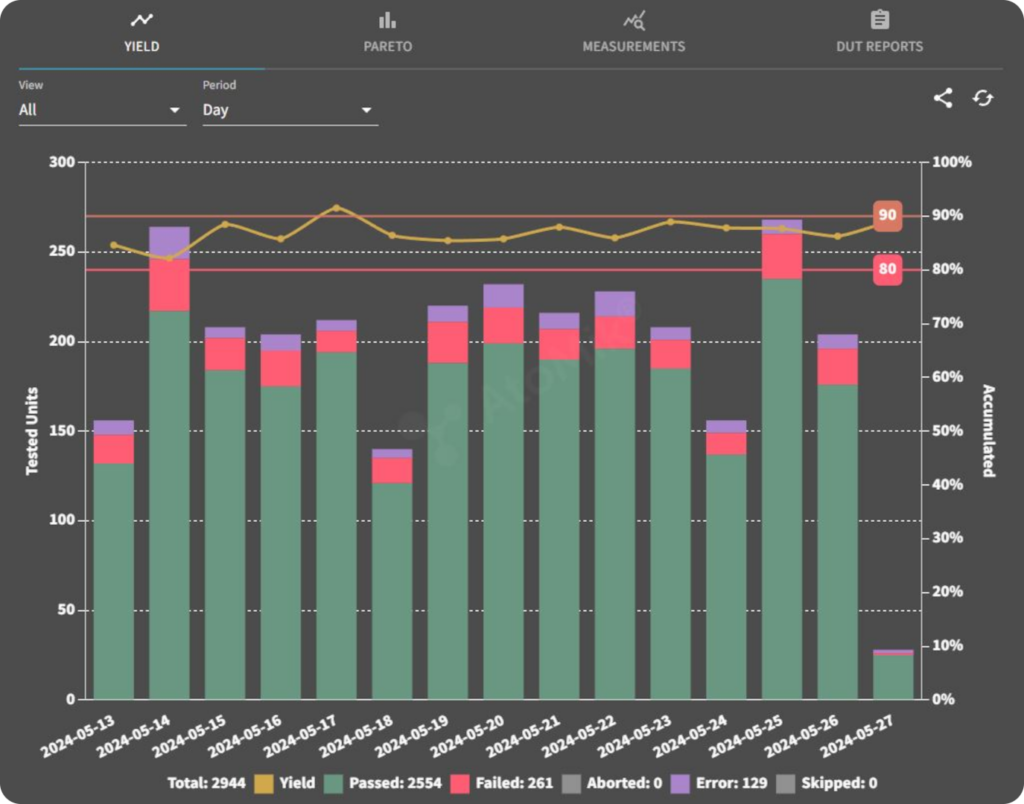
Finally, good data visualization software is essential, with plots and statistics quickly telling what to focus on.
Contact us today if you want to learn more or get a quote for your RF test system!

